|
| Fasciola hepatica egg Photo/CDC |
General Information
· Fasciola hepatica is a trematode or fluke also known as the “sheep liver fluke”
· All trematodes are parasitic
· All trematodes have a phase of their life cycle in snail or other molluscan host
· All trematodes are associated with water
· Facioliasis is a zoonotic disease
Geography
· Human infection has been reported from over 60 countries, mainly in sheep-raising areas
· Important public health problem in Latin America (Peru, Bolivia, Cuba), Russia, parts of Europe and Iran
· Reported sporadically in the US
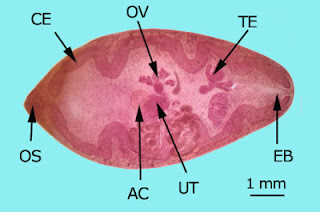
Morphology (adults)
· Leaf-shaped with cephalic cone
· 3.0 x 1.3 cm
Morphology (eggs)
· Large, ovoid, thin-shelled, operculated, yellowish-brown in color
· 130-150 x 90 um in size
Life Cycle
· Adult fluke in biliary passages
· Immature eggs are discharged in feces
· Eggs embryonate in the water
· Eggs hatch and release miracidia
· Miracidia invade suitable snail host (intermediate host)
· Development in snail (sporocyst>rediae>cercariae)
· Cercariae leaves snail and encyst on aquatic vegetation as metacercariae
· Metacercariae on uncooked water plant is ingested by human, sheep or cattle (F. gigantica)
· Metacercariae excyst in the duodenum
· Migrates through intestinal tract, peritoneal cavity and liver parenchyma into bile ducts
· Matures into adults
· Maturation from metacercariae to adult fluke takes up to 4 months
· In humans, adult flukes can produce eggs for 9 years
Pathology
· Migrating flukes can cause abdominal pain, liver enlargement and fever
· Blockage of bile ducts, portal cirrhosis, eosinophilia, jaundice, diarrhea and anemia
· Halzoun: In humans that eat raw sheep liver. Adult flukes leave liver and attach to throat causing blockage
Diagnosis
· In endemic areas, symptoms suggest infection
· History of eating uncooked watercress and water lettuce
· Finding eggs in feces or biiary drainage. Eggs of F. hepatica and Fasciolopsis buski too similar to differentiate. Check travel history.
· Antibody detection: enzyme immunoassays (EIA) with excretory-secretory (ES) antigens combined with confirmation of positives by immunoblot
Treatment
· The drug of choice is triclabendazole with bithionol as an alternative
Epidemiology
· Sheep-raising countries (and cattle) where there is a suitable snail host (Lymnea sp).
· Where humans eat uncooked watercress and other aquatic plants in salads or on sandwiches
Prevention and Control
· Educate public in endemic areas not to eat wild (uncooked) watercress and other water plants
· Avoid using livestock feces to fertilize water plants
· Treat animal infections
· Using molluskicides
Other Information
· False fascioliasis (pseudofascioliasis): this is the presence of eggs in the stool resulting not from an actual infection but from recent ingestion of infected livers containing eggs.
· Have the patient follow a liver-free diet several days and repeat stool examination.
 |
| Adult Fasciola hepatica Photo/Adam Cuerden via Wikimedia Commons |